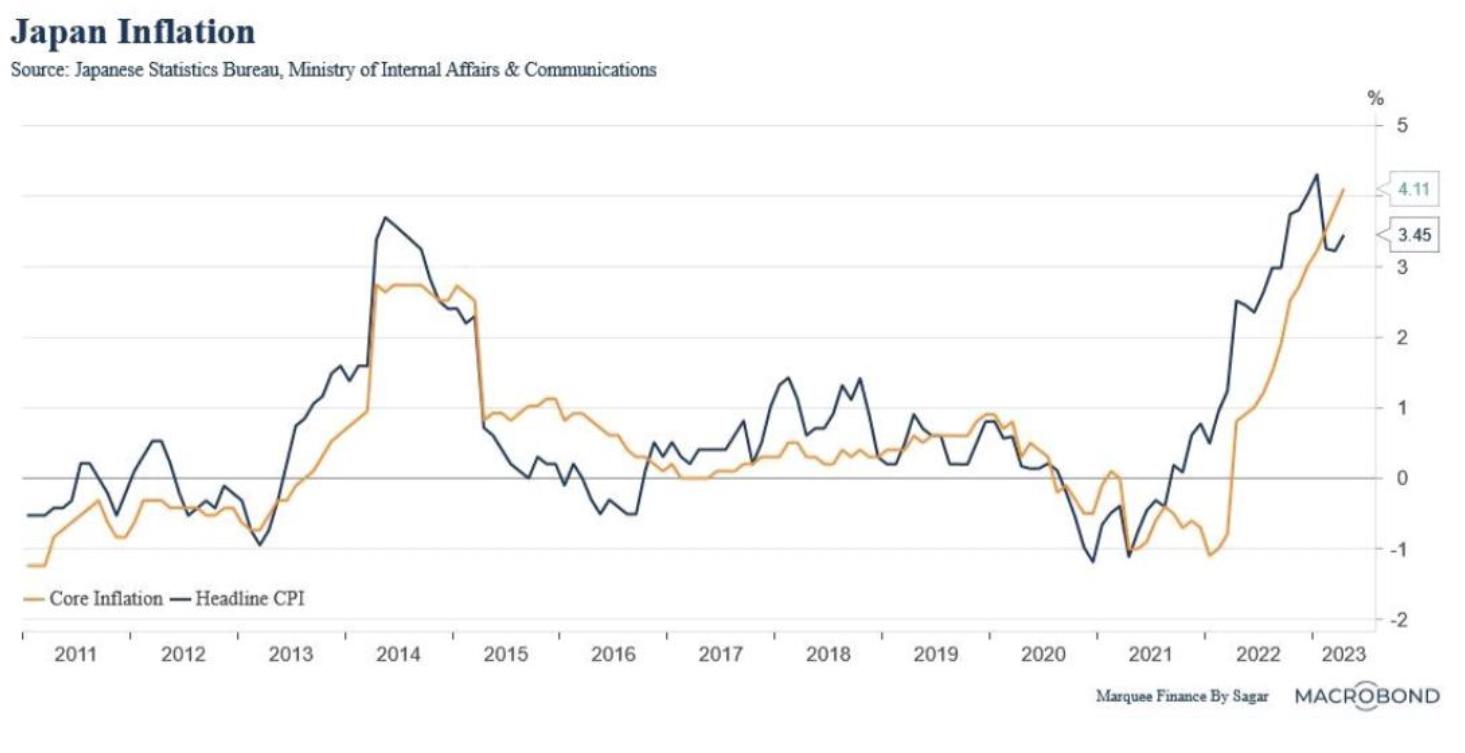
Japan’s economy has been struggling with deflation and low growth for decades, despite the efforts of the Bank of Japan (BOJ) to stimulate demand and inflation through ultra-loose monetary policy. However, recent data suggests that Japan’s inflation is finally picking up, driven by higher commodity prices, supply bottlenecks, and stronger domestic demand https://www.msn.com/en-us/money/markets/japans-inflation-stays-above-bojs-target-key-gauge-hits-four-decade-high/ar-AA1bnYbU https://asia.nikkei.com/Economy/Inflation/Japan-inflation-spreads-to-services-as-key-index-hits-41-year-high.
According to the latest data, Japan’s core consumer inflation, which excludes fresh food but includes energy items, rose 3.4% year-on-year in April 2021, matching market expectations and accelerating from a 3.1% gain in March https://www.msn.com/en-us/money/markets/japans-inflation-stays-above-bojs-target-key-gauge-hits-four-decade-high/ar-AA1bnYbU. It was the highest inflation rate since September 2014, when a sales tax hike boosted prices https://www.msn.com/en-us/money/markets/japans-inflation-stays-above-bojs-target-key-gauge-hits-four-decade-high/ar-AA1bnYbU. A key index stripping away the effects of both fresh food and fuel, which is closely watched by the BOJ as a key barometer of domestic demand-driven price trends, rose 4.1% year-on-year in April, marking the fastest annual pace since September 1981 https://www.msn.com/en-us/money/markets/japans-inflation-stays-above-bojs-target-key-gauge-hits-four-decade-high/ar-AA1bnYbU.
The implications of Japan’s inflation for world bond and currency markets are:
• World bond markets may face upward pressure on yields and downward pressure on prices, as Japan’s inflation may reduce the demand for low-risk assets such as government bonds. Japan is one of the largest holders of foreign bonds, especially US Treasuries, and if it shifts its portfolio away from bonds to other assets with higher returns, it may cause a sell-off in global bond markets https://asia.nikkei.com/Economy/Inflation/Japan-inflation-spreads-to-services-as-key-index-hits-41-year-high https://www.msn.com/en-ph/news/money/japan-inflation-34-in-april/ar-AA1bpH28. Moreover, if Japan’s inflation prompts the BOJ to tighten its monetary policy sooner than expected, it may also cause a rise in Japanese bond yields and a decline in bond prices https://asia.nikkei.com/Economy/Inflation/Japan-inflation-spreads-to-services-as-key-index-hits-41-year-high https://www.msn.com/en-ph/news/money/japan-inflation-34-in-april/ar-AA1bpH28.
• World currency markets may face a strengthening of the Japanese yen and a weakening of other major currencies, such as the US dollar and the euro. Japan’s inflation may increase the attractiveness of the yen as a store of value and a hedge against inflation, especially if it outpaces the inflation rates of other countries https://asia.nikkei.com/Economy/Inflation/Japan-inflation-spreads-to-services-as-key-index-hits-41-year-high https://www.msn.com/en-ph/news/money/japan-inflation-34-in-april/ar-AA1bpH28. Moreover, if Japan’s inflation leads to a narrowing of the interest rate differential between Japan and other countries, it may also increase the demand for the yen and reduce the demand for other currencies https://asia.nikkei.com/Economy/Inflation/Japan-inflation-spreads-to-services-as-key-index-hits-41-year-high https://www.msn.com/en-ph/news/money/japan-inflation-34-in-april/ar-AA1bpH28.
These are some possible implications of Japan’s inflation for world bond and currency markets. However, these implications are not certain or inevitable, as they depend on various factors, such as the magnitude and persistence of Japan’s inflation, the reactions of other central banks and governments, and the expectations and sentiments of market participants. Therefore, it is important to monitor the developments and trends of Japan’s economy and its impact on global financial markets.