The public is always ready to panic over the next pandemic. We love a good movie like the old Ebola scare, Outbreak. We even have a name for the next mystery disease — the big one that is supposed to destroy us all like World War III or like the apocalypse — a scientific name. The World Health Organization has designated it with the generic place holder “Disease X.” But is its real name “COVID-19” as the latest coronavirus has just specifically been named?
Mainstream media, often instrumental in creating health scares, is whipping up concern that the latest coronavirus (there have been many coronaviruses over the years), recently given the name COVID-19, might be that pandemic. What do they actually know?
The incidence and death rate of coronavirus (COVID-19) compared to the common flu
The World Health Organization cautioned years ago that a mysterious “disease X” could spark an international contagion. The new coronavirus illness, with its ability to quickly morph from mild to deadly, is emerging as a contender.
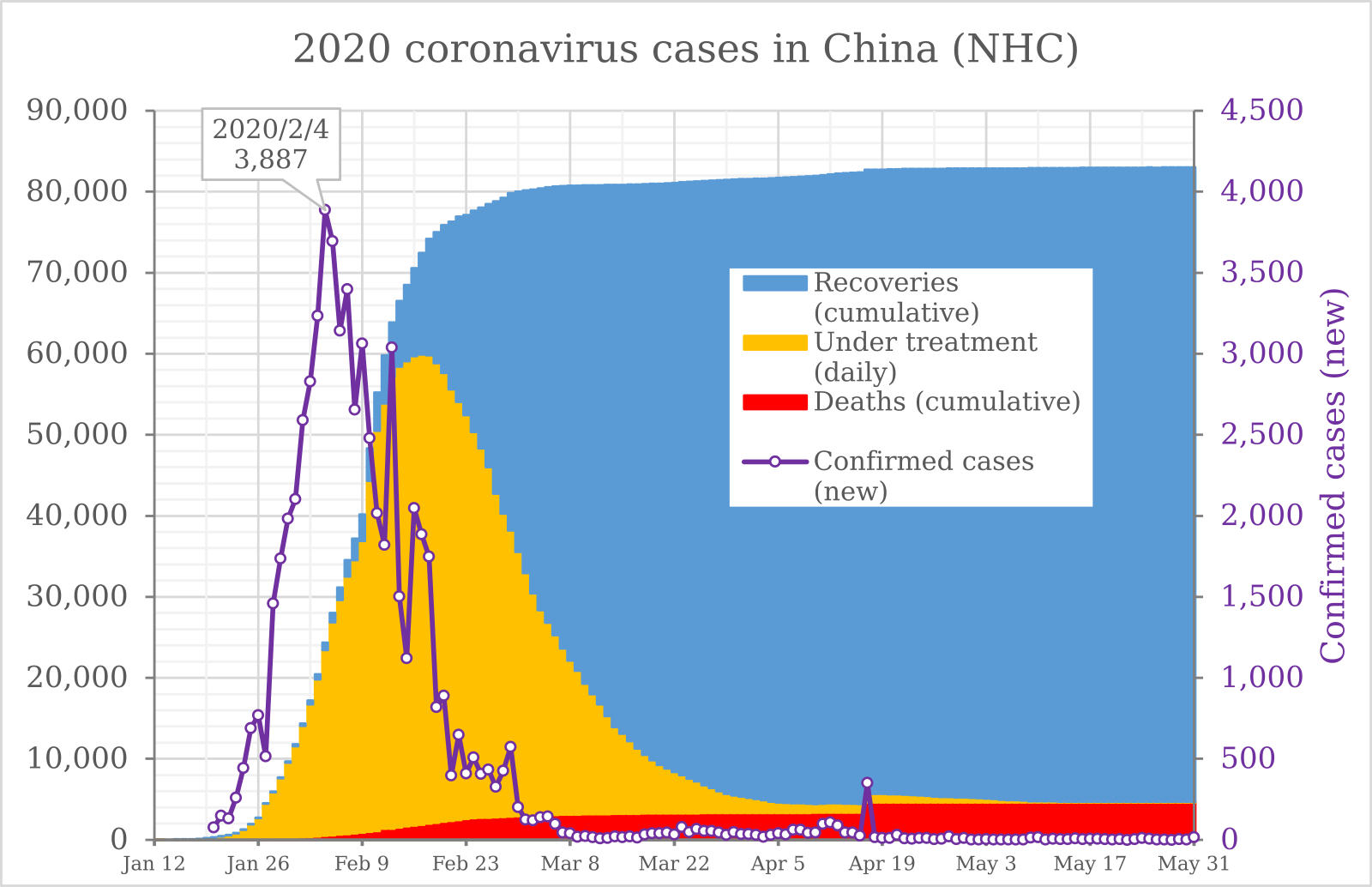
From recent reports about the stealthy ways the so-called Covid-19 virus spreads and maims, a picture is emerging of an enigmatic pathogen whose effects are mainly mild, but which occasionally — and unpredictably — turns deadly in the second week. In less than three months, it’s infected almost 78,000 people, mostly in China, and killed more than 2,300….
“Whether it will be contained or not, this outbreak is rapidly becoming the first true pandemic challenge that fits the disease X category,” Marion Koopmans, head of viroscience at Erasmus University Medical Center in Rotterdam, and a member of the WHO’s emergency committee, wrote Wednesday in the journal Cell.
The disease has now spread to more than two dozen countries and territories. Some of those infected caught the virus in their local community and have no known link to China, the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention said.
It all sounds scary when the alarm is sounded by people so high up in the medical food chain and is carried outside the alternative “conspiracy” press, but it is probably more the unknownaspects of this new disease that scares us. It often is fear of the unknown because our imaginative minds readily fill in the blanks with adrenaline-pushing scenarios.
The numbers sound high even without medical commentary. In Hubei Province, where the disease began, the death rate has been about 2.9%. However, in some other provinces where it has been less prevalent, the death rate has been as low as 0.4%.
The death rate soars to 14.8% in those 80 and older; among those ages 70 to 79, the COVID-19 death rate in China seems to be about 8%; it’s 3.6% for those ages 60 to 69; 1.3% for 50 to 59; 0.4% for the age group 40 to 49; and just 0.2% for people ages 10 to 39. Nobody 9 and under has died of this coronavirus to date.
However, when held up against influenza — the common flu (nothing but a nickname for “influenza”) — they pale to utter insignificance. Influenza, as a standard measure everyone is familiar with, has a death rate each year of around 1%, but the infection rate is very much higher than COVID-19. Also, the death rates of newly discovered viruses tend to run higher at first because only the most obvious cases are caught. Many scientists have already said they expect the death rate of coronavirus to drop as we see a broader number of cases and as treatments are developed.
Bear in mind, too, that the influenza death rate is suppressed because we have a vaccine that, while it does not seem very effective in preventing the disease, does ready the body to handle it. We particularly give that vaccine to older people who are more susceptible to dying from the common flu (or common cold — often the same thing).
Influenza has a certainty about it that makes it far less frightening. We know it as a familiar cohabitant of our world that will hit us in a massive wave every year. In spite of the size of its assault, we know what to expect from it every year. We know that we are a huge herd, and that this viral predator will only single out and kill the weakest in the herd.
The rate at which influenza spreads is actually much greater than what we are seeing with coronavirus. However, that may be due to the fact that extreme quarantine efforts have contained COVID-19 — efforts that we make because of how frightened so many are of this new disease due to it’s unknown risks. No one, on the other hand, bothers to contain the common flu. We readily go all over town and share it with everyone everyday, taking only modest precautions at best. We also know that the flu will go away on its own when spring comes. We don’t know that about the new coronavirus. What if it spreads faster and keeps doing so all year?
The number of people routinely infected by influenza is absolutely massively greater than by COVID-19. This year, alone, influenza has already infected twenty-six-million people … in just the US alone! Twenty-six-million! And this completely ordinary flu epidemic isn’t even over yet! It is extremely doubtful COVID-19 could ever catch up this year with the number of infections already in play from influenza.
The symptoms and dangers of coronavirus (COVID-19) compared to the common flu
The symptoms of the two types of disease are almost identical. Both affect the sinuses, the the throat, the bronchial tubes and lungs to varying degrees and sometimes cause stomach upset or diarrhea.
COVID-19, in fact, causes only mild symptoms in about 80% of the people it infects (simple cold-like symptoms). On the other hand, it tends not to present the upper respiratory symptoms as often as the flu and to lean harder, instead, on the lower respiratory system, which is more dangerous. It is, in fact, not easy to distinguish between the two kinds of virus based on symptoms. They are that close.
About 5% of patients have critical illness, including respiratory failure, septic shock and multi-organ failure.
That sounds frightening, BUT …
Of those twenty-six-million people (in just the US) who are infected right now with influenza A or B, influenza has already hospitalized a quarter-of-a-million and killed fourteen thousand! We should be scared to death of this monster virus called “influenza.”
Like the new coronavirus, influenza results in cases of pneumonia in a small number of people — mostly “walking pneumonia,” meaning quite simply pneumonia that is not too severe to keep you from going about your daily business. Of those with pneumonia, a similar percentage of people with influenza become critical and are bedridden as occurs among those with the new coronavirus, and a similar percentage of the critical people wind up dying — mostly the old and infirm, sometimes infants. Oddly (and fortunately) COVID-19 does not seem to impact infants as much as adults.
Older adults, especially those with chronic conditions, such as hypertension and diabetes, have been found to have a higher risk of severe illness.
That, too, is just like influenza.
Hundreds of articles just like the Bloomberg one I led off with came out in the mainstream media and alt press during the Ebola scare, too. Yet, we are still here. Everyone was every bit as concerned as right now, and doctors were rushing around the world to combat it.
Why did the Ebola epidemic turn out just fine? Because situations are dynamic. Doctors work hard to attack the virus on all fronts like firefighters. They may contain the “blaze,” or they may not. When they don’t, it often goes out on its own because the season changes, just as happens with some massive forest or brush fires that are out of human control when the rainy season hits and puts out what humans could not. Nature has its ways … both of killing and of sparing.
Is COVID-19 likely to become a global pandemic?
The risk of Disease X is always there with any new highly contagious virus, but there are always dynamics battling down that risk.
Because of its characteristics, the COVID-19 outbreak is being considered potentially as deadly as one of the worst influenza outbreaks in history, known as the Spanish Flu of 1918. Consider, however the extreme medical difference of our times in terms of the medications and research we can throw at the disease, the number of hospitals and maybe even the general health of the population. All of that probably reduces the pandemic risk well below what was seen in the 1918 Spanish Flu pandemic.
COVID-19 is also far less deadly than SARS, which caused a similar scare af few years ago and had a 9.5% fatality rate. SARS is still a deadly disease, but is fairly well under control.
The risks from COVID-19 right now are being seriously overhyped by media. That, in part, happens because percentage increases (such as the spread doubling in a day) are easy when the numbers of infected are low. It’s easy to double 1,000 infected people in a day, but a lot harder to double half a million in a day. That’s just a game numbers play with us. Thus, the media right now is presenting all kinds of hockey-stick graphs.
What is the biggest danger right now from the coronavirus?
With all of that said about the health risks that are actually known, none of it has much bearing on how devastating the virus can actually be economically because the big factor economically is fear and human response.
Ironically, that is how coronavirus kills the body. It causes an overreactive immune response in the lungs and other tissues that inflame those organs, plug them up with human secretions, and damage them. We risk creating such an overreactive response in the macro-sphere as well with our human reactions, making us more deadly to ourselves than the disease!
We are the ones who determine how much fear shuts down sales, transportation, production, hospitality, etc. And, on that front, the new virus is already having a hay day, which I will detail in my next article.
For the time being, the true danger of coronavirus is fear itself. I think the unprecedented response of the Chinese government in quarantining millions of people in several major cities has limited the disease but thrown gasoline on the fear.
The response has created a lot of questions as to why China is reacting so intensely. Does the government know, perhaps, that this is an engineered virus that escaped a local laboratory — one created for germ warfare? Was it just an engineered carrier for worse diseases — something relatively harmless that is made to be highly infectious that can be modified to deliver death? Did the Chinese government perhaps not know whether the version that escaped was just the blank carrier or one augmented into or with a military-grade disease? We know such hazards as human-engineered diseases are possible even in the present situation. It is the unknown that scares us. Our minds abhor a vacuum and seek to fill it. And, if to fill it, then to fill it with something spectacular. That is how conspiracy theories are born.
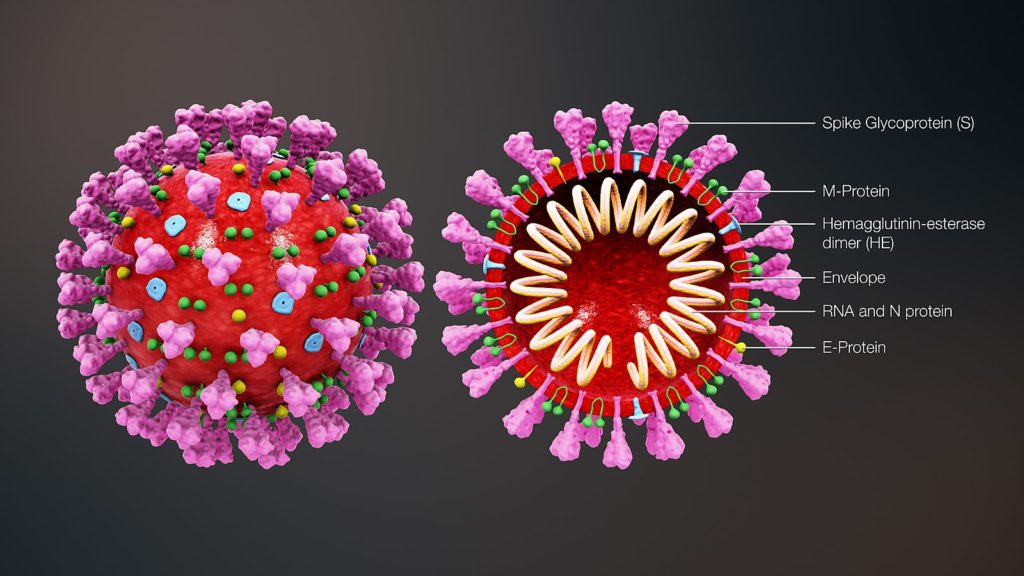
However, so far the facts we know about the coronavirus with certainty are not all that firework spectacular. (Other than how the virus looks. It gets its name from its starburst, sunlike corona.) We need to be careful because of the unknown, but fear of the unknown can hurt us more than the disease, itself. Our own social immune response can hurt us. That is exactly how the virus gets the body to injure itself with an overblown response. So, let’s not give it more than its due on the outward social part of our lives.
In my next article I’ll lay out in detail how human fear, and not the damage from the disease itself, is already causing major human suffering and economic destruction.
Here are the latest COVID-19 counts for every nation:
Coronavirus COVID-19 Global Cases by Johns Hopkins CSSE