by OkIncident5269
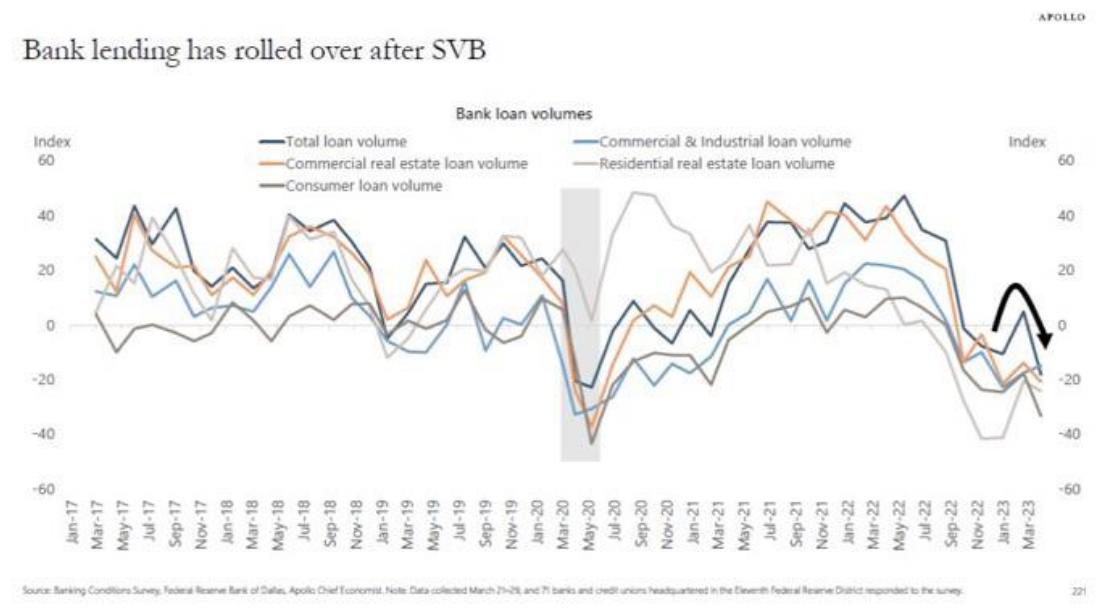
JP literally said he was going to rely on bank lending tightening to act as an alternative to raising rates.
This was 100% forecasted. Banks are down $600b, the last thing they want to do is increase their risk profile.
It just happens to perfectly coincide with the Feds mandate of lowering inflation to keep a healthy economy. Take away lending, demand eases, inflation drops.
…but really it’s just about the banks self-preservation at this stage.
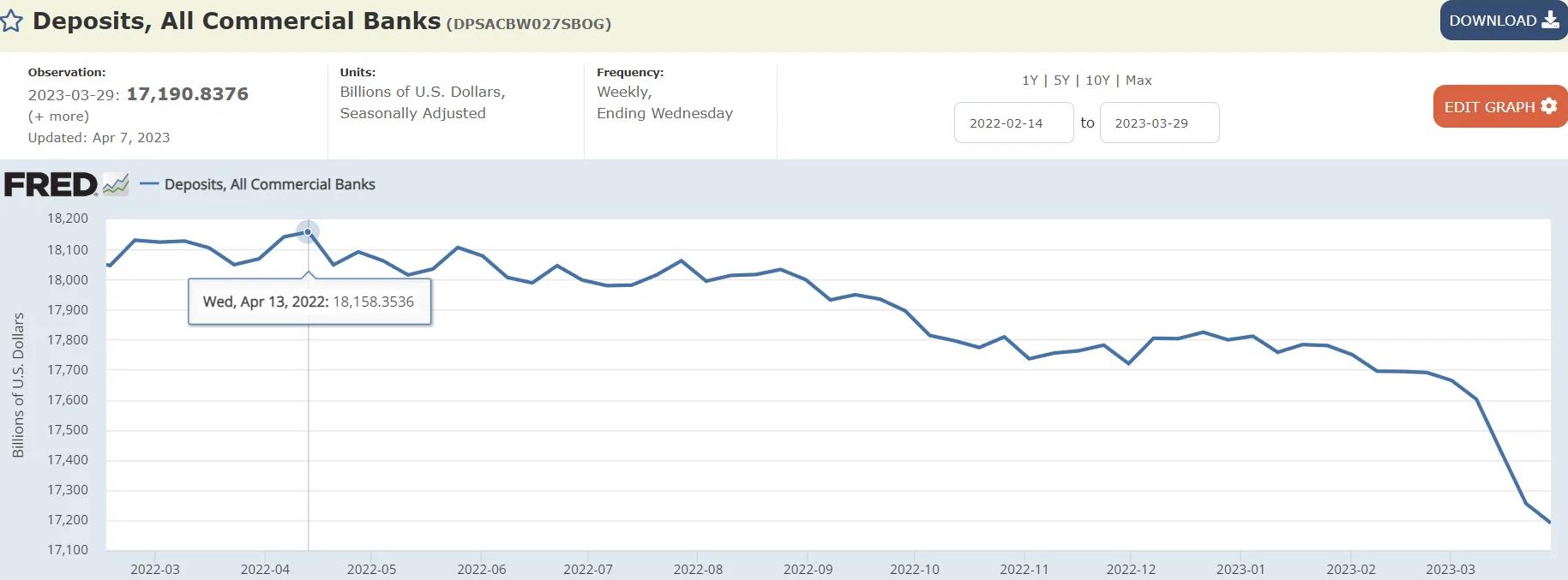
Actually bank deposits are now down nearly a trillion from the peak a year prior. This according to FRED’s own data. Fear the damage being done to small/regional banks and by extension commercial real estate markets.
Interestingly, the same thing happened in 2008, a few months before the GFC and couple months after the collapse of Bear Stearns. Banks don’t pull back on lending unless there are major fears that people won’t be able to pay the loans back
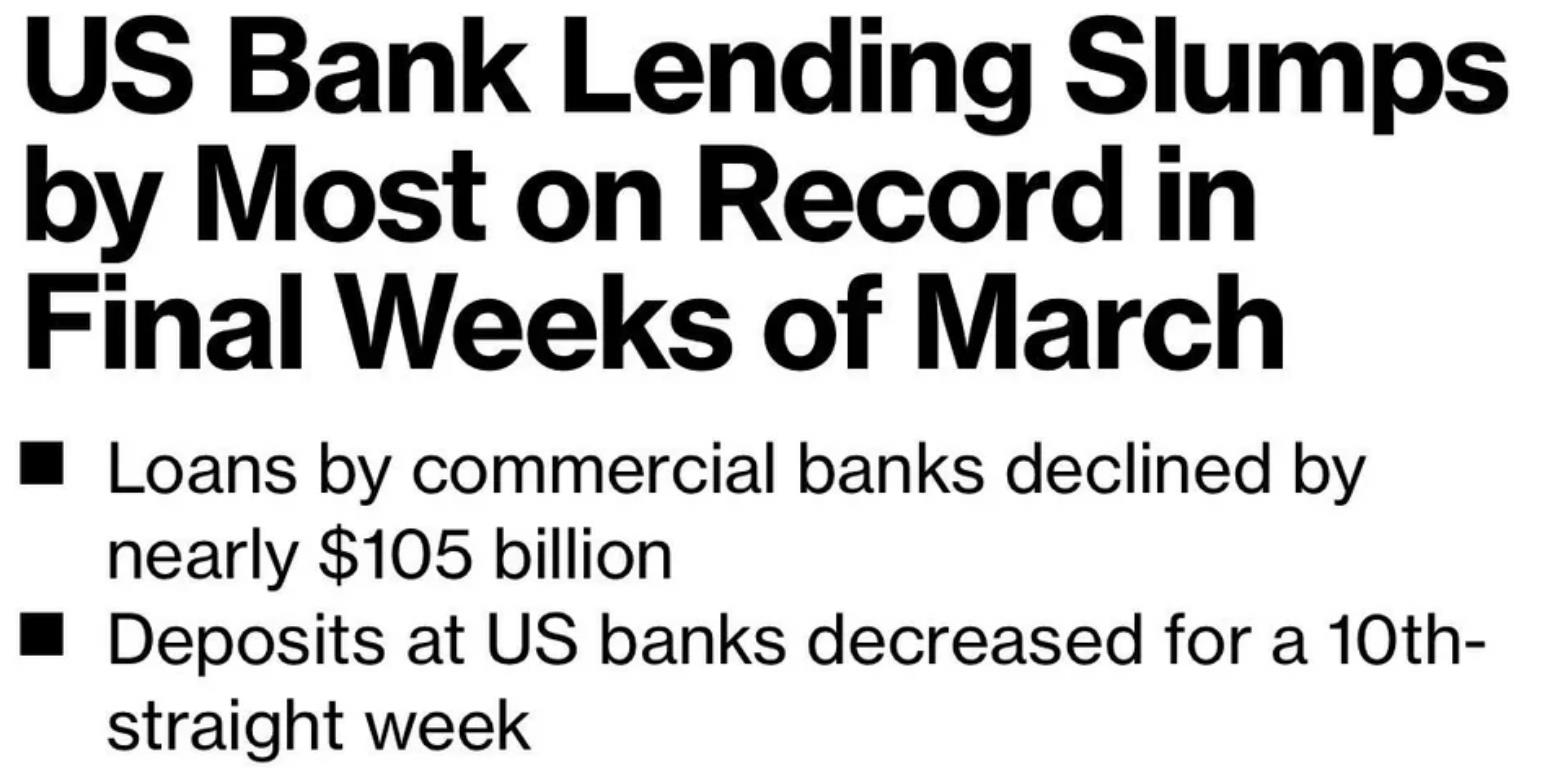
Source www.reuters.com/article/sppage012-n05528226-oisbn-idUSN0552822620080505

Financial crisis brewing in the “Shadow banking system” (pension funds, insurers, mutual funds, hedge funds etc).
London
CNN
—
The International Monetary Fund warned this week of “vulnerabilities” among so-called non-bank financial institutions, saying global financial stability could hinge on their resilience. The Bank of England called attention to the same issue last month.
And global investors surveyed by Bank of America in the middle of the recent banking crisis pointed to a group of US non-banks — rather than traditional lenders such as the newly defunct Silicon Valley Bank — as the most likely source of a credit crisis.
But what exactly are non-banks and how risky are they?
The term encompasses financial firms, other than banks, that provide all manner of financial services, including lending to households and businesses. It’s a diverse cast list: non-banks range from pension funds and insurers, to mutual funds and high-risk hedge funds.
And the sector is big. According to the Financial Stability Board (FSB), a body of global regulators and government officials, non-banks had about $239 trillion on their books in 2021, accounting for just under half of the world’s total financial assets.
edition.cnn.com/2023/04/06/business/non-banks-shadow-banks-risks-explainer/index.html